Rethinking 3D Reconsctruction
1. SFM(Structure From Motion)
- Feature Extraction
- Find keypoints:
- Scale-Space Construction: blur the image and generate a set of images -> Result: At this point, the computer possesses a “comprehensive set” of images ranging from clear to blurry, and from large to small.
- Keypoint Localization: difference of gaussian, extreme detection -> Results: Blobs or Corners.
- Find keypoints:
- Feature Matching
- Descriptor Matching: Calculate feature vectors for each keypoint, compare them across images, and remove outliers using geometric constraints (RANSAC).-> Result: Verified Correspondences (pairs of points linking Image A to Image B).
- Sparse Reconstruction
- Triangulation & Optimization: Project 2D matches back into 3D space (Triangulation) and refine via Bundle Adjustment.
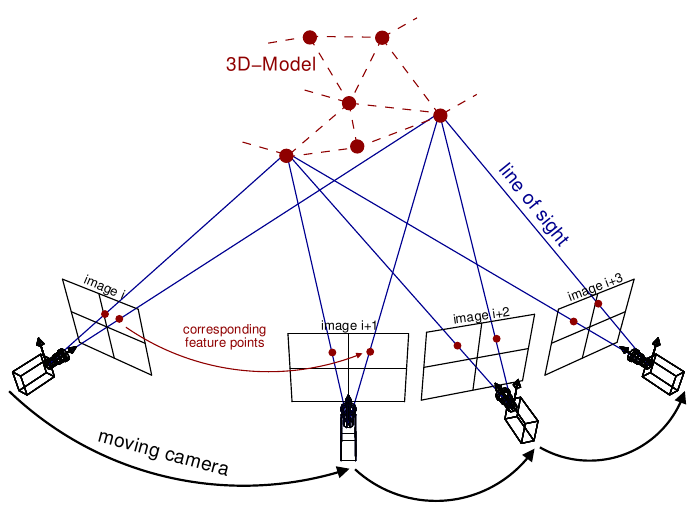
- Triangulation & Optimization: Project 2D matches back into 3D space (Triangulation) and refine via Bundle Adjustment.
2. NeRF (Neural Radiance Fields)
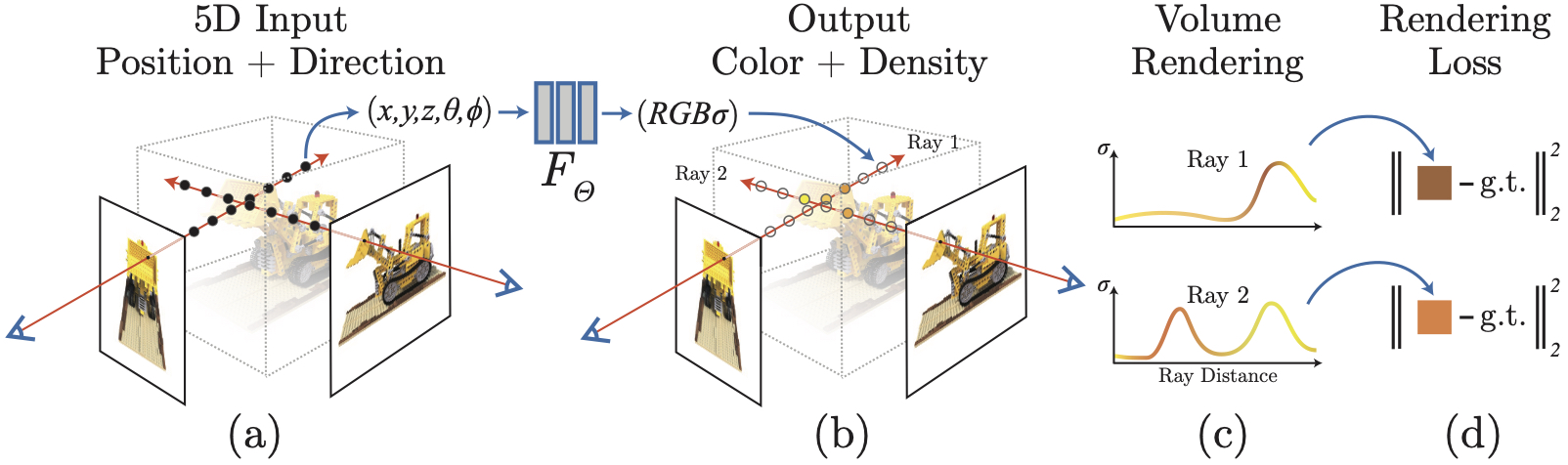

-
Ray Sampling
For every pixel, NeRF casts a ray into the scene and samples a set of 3D points along the ray. -
A Model to Predict Density and Color
The core of NeRF is an MLP that maps each sampled 3D point (plus viewing direction) to:- σ (density)
- RGB color
This allows NeRF to represent both geometry and appearance.
-
Volume Rendering
NeRF integrates colors and densities using a volume rendering equation to compute the final pixel color.
Points with higher density occlude points behind them, and contributions are accumulated along the ray.
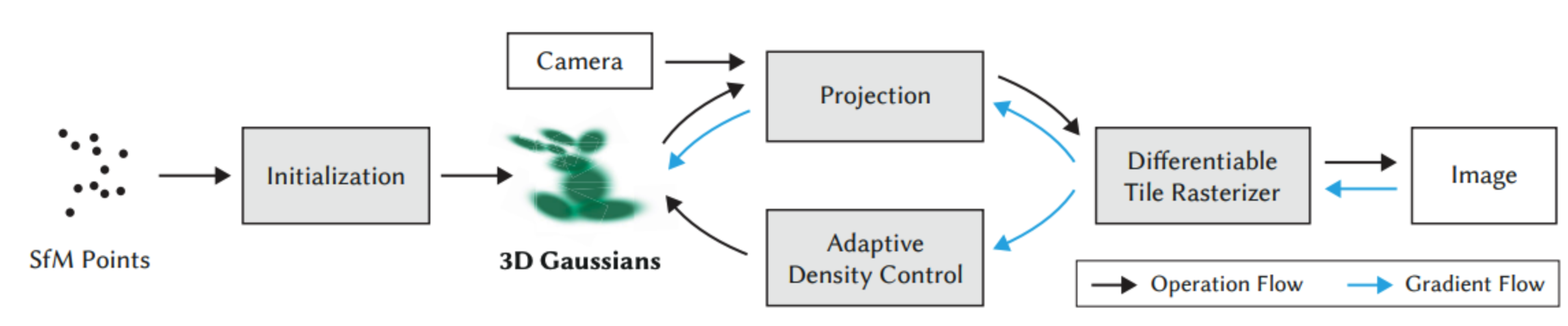
3. Gaussian
-
Initialization
Start with a sparse point cloud generated via SFM (Structure from Motion). These points serve as the initial means (positions) for the 3D Gaussians.
-
Gaussian Representation: Geometry (Position & Shape)
Each point is represented as a 3D anisotropic Gaussian (an ellipsoid). To make this differentiable and valid, the covariance matrix $\Sigma$ (which defines shape) is decomposed into:Scaling ($S$): How much to stretch the ellipsoid along 3 axes.Rotation ($R$): Represented by a quaternion to define orientation.
-
Gaussian Representation: Appearance (Color & Opacity)
To capture realistic visuals, each Gaussian carries:Opacity ($\alpha$): How transparent or solid the ellipsoid is.Spherical Harmonics (SH): Coefficients that represent view-dependent color (allowing for shiny surfaces and lighting effects that change as you move the camera).
-
Differentiable Rasterization
a fast rasterization approach:
- Projection: 3D Gaussians are projected into 2D screen space (becoming 2D splats).
- Sorting: Splats are sorted by depth (front-to-back) using a fast GPU Radix sort.
- Alpha Blending: The sorted splats are composited to form the final image.

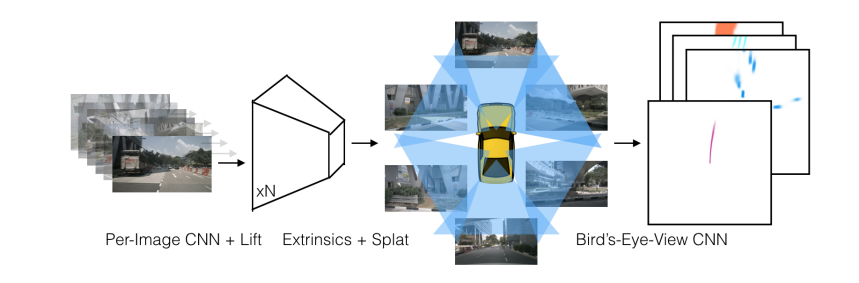
4. LSS
- Lift
Each pixel feature corresponds to a 3D ray.
LSS predicts a probability distribution over depth bins for every pixel.
Then each pixel is lifted into multiple possible 3D positions using camera intrinsics/extrinsics.
-
Splat
All lifted 3D features are projected (“splatted”) onto a 2D BEV(bird’s eye view) ground.
Features falling into the same BEV cell are aggregated, producing a BEV feature map. - Shoot
Once BEV features are obtained, it could be feed into diffrent heads for different downstream tasks:- 3D object detection
- BEV segmentation
- Road layout prediction, etc.
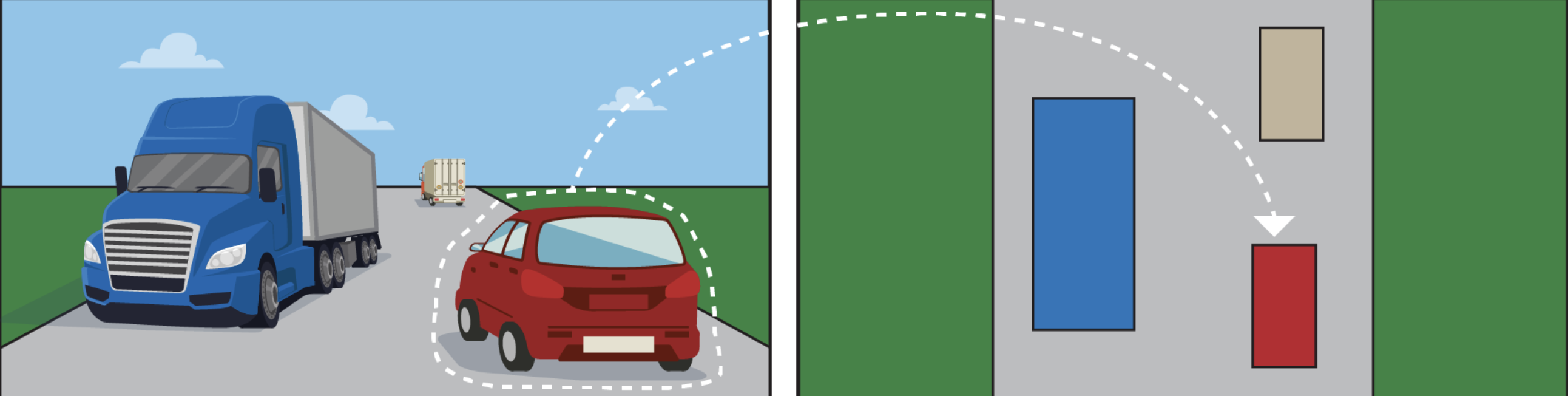
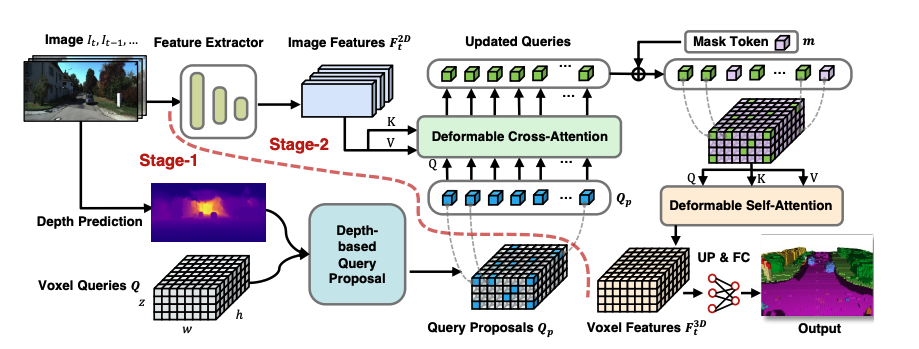
5. Occupancy Prediction
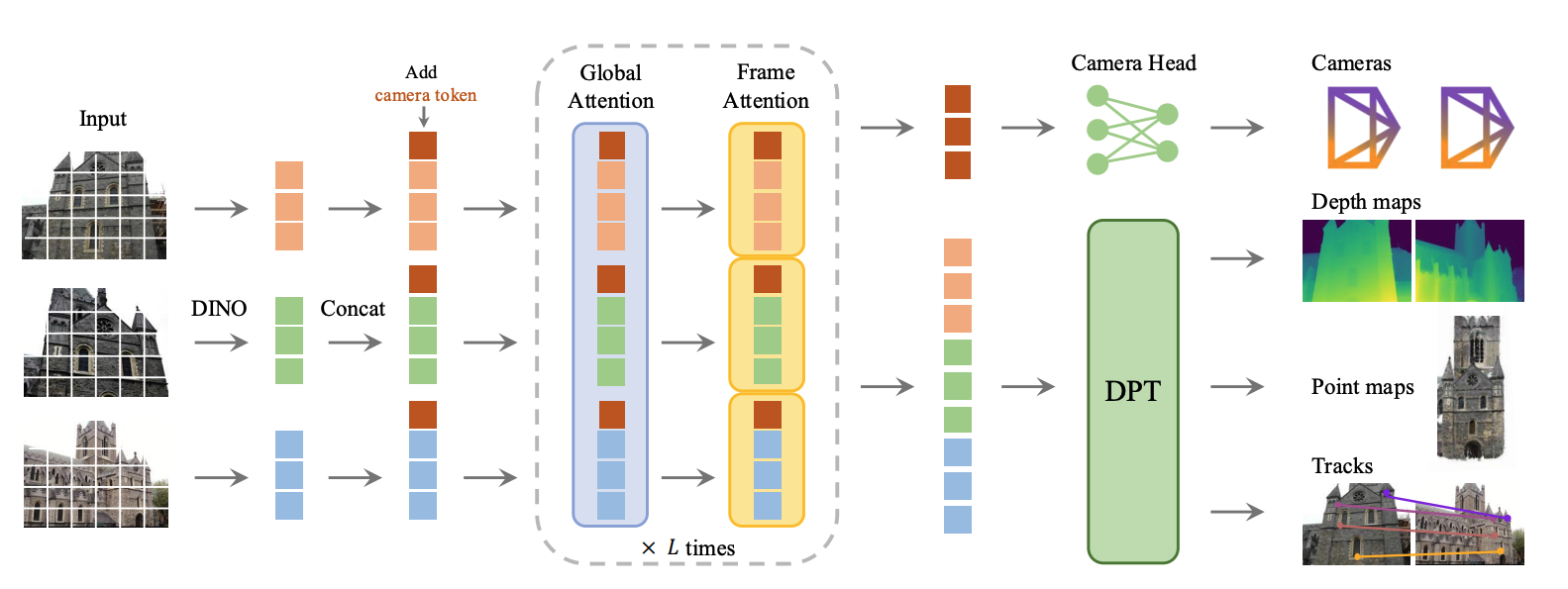
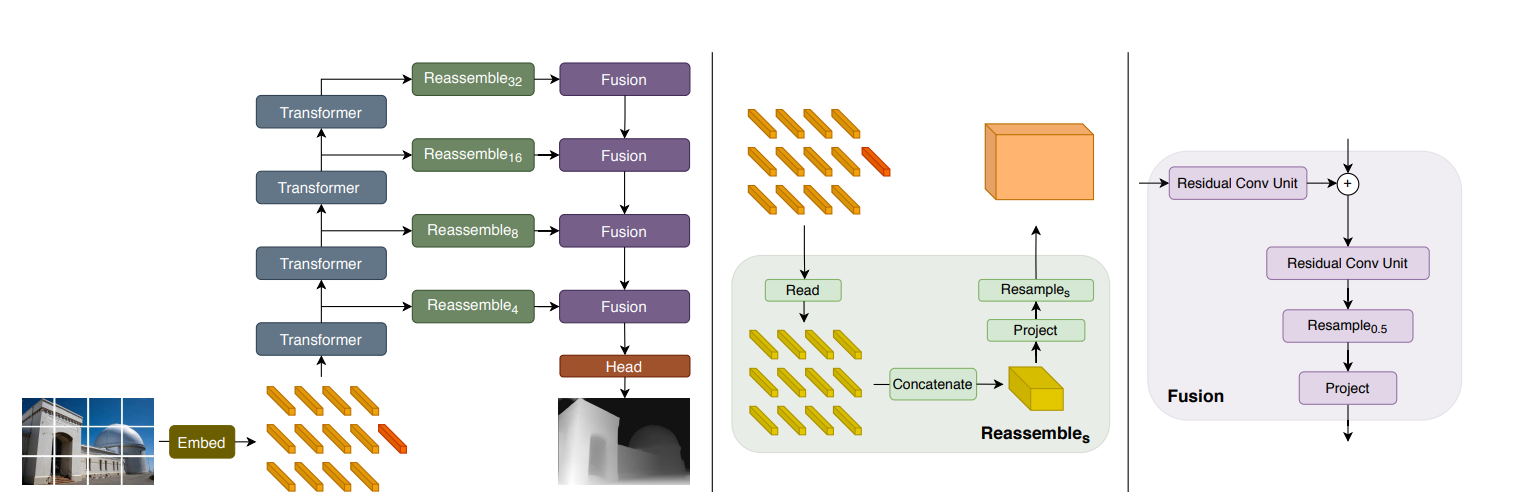
6. End2End: VGGT