Double the Fun:How to Seamlessly Run VMware on Your Ubuntu System
In this comprehensive tutorial, I’ll delve deep into the step-by-step process of setting up VMware on an Ubuntu system. Whether you’re a beginner looking to explore the virtualization world or an experienced user aiming to streamline your workflow, this guide is tailored to ensure a smooth installation experience. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to harness the power of VMware on your Ubuntu machine.
0. Prerequisite
- System Compatibility:
VMware Workstation requires a 64-bit processor and 64-bit host operating system.
- Hardware Requirements:
At the very least, you’ll need a 1.3GHz or faster core speed, but a multi-core processor is recommended for best performance. Ensure you have adequate RAM (minimum 2GB, 4GB or more recommended) and around 1.5GB of available disk space for the application, plus additional space for virtual machines.
1. Download VMware & Ubuntu Iso
VMware offers VMware Workstation Player for non-commercial use, which is a great option if you’re looking to explore its features without any financial commitments.
- Visit the Official VMware Website:
Navigate to VMware’s official website to ensure you’re getting the genuine software.
 Click “Try Workstation 17 Player for Linux” and a ‘.bundle’ file should be automatically downloaded.
Click “Try Workstation 17 Player for Linux” and a ‘.bundle’ file should be automatically downloaded.
- Visit Ubuntu Official Website for a Clean Iso
Select a Version you like, personally I recommend version with ‘LTS’ postfix, for it stands for ‘Long Time Support’.
2. Install VMware
- Dependencies for Installation:
Install gcc, Cmake, and vmware-modconfig
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install gcc
sudo apt install make
Then install VMware and compatible dependencies
chmod +x VMware-Workstation-Full-<version>.bundle
sudo ./VMware-Workstation-Full-<version>.bundle
sudo vmware-modconfig --console --install-all
Many online tutorials skip a vital configuration step when installing VMware on Ubuntu, leading to startup problems. Our guide emphasizes this critical configuration to ensure a hassle-free VMware experience.
3. Create New Virtual Machine
Once you’ve started VMware, initiate the creation of a new virtual machine. Make sure to select the ISO file you’ve recently downloaded as the source for the virtual machine installation.
4. Hello Ubuntu inside Another Ubuntu
Use ‘Ctrl+Alt+T’ to call out the terminal
echo "Hello, Ubuntu inside another Ubuntu!"
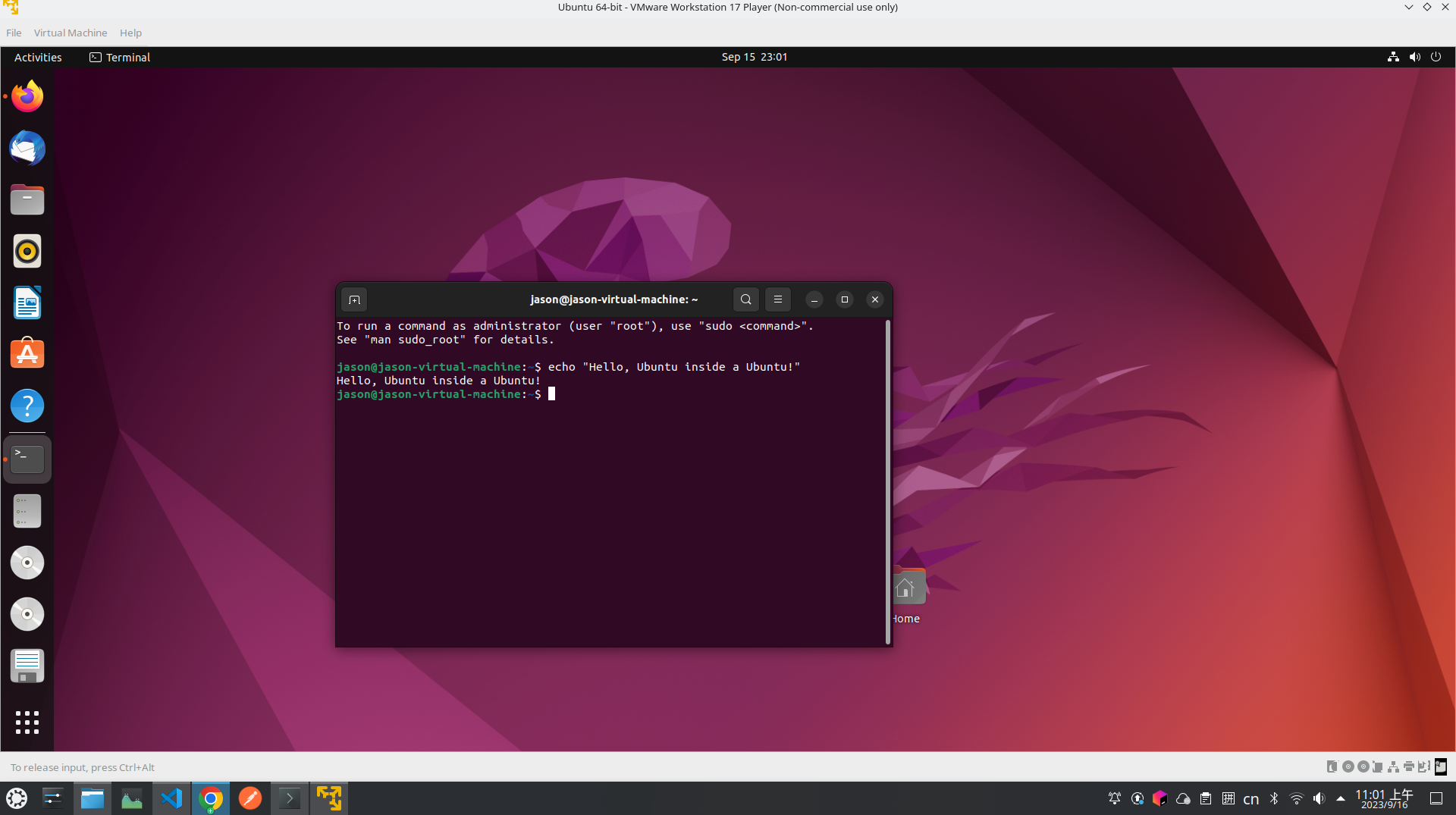 Should work like this!!
Should work like this!!